Programming Language
JS33 - 29.알고리즘
양찬우
2021. 11. 9. 18:08
728x90

- 알고리즘을 마스터하기 위해선 데이터 구조에 대한 명확한 이해가 필요하다.
- 일반적으로 고려해야 할 사항
- 필요한 변수
- 반복 횟수, 종류
- 사용가능한 빌트인 메서드
- 고려해야 할 에지 케이스
- 헬퍼 함수를 추출하거나 추상화할 수 있는가?
- 확장성이 있는가? input 크기가 커지면 어떻게 실행되는가?
- 캐싱 메커니즘이 필요한가?
- 성능 향상과 메모리 최적화
- 코드 리팩터링과 재사용 기회가 있는 코드를 작성하기
- 커링을 통한 파라미터 제거
정렬 알고리즘
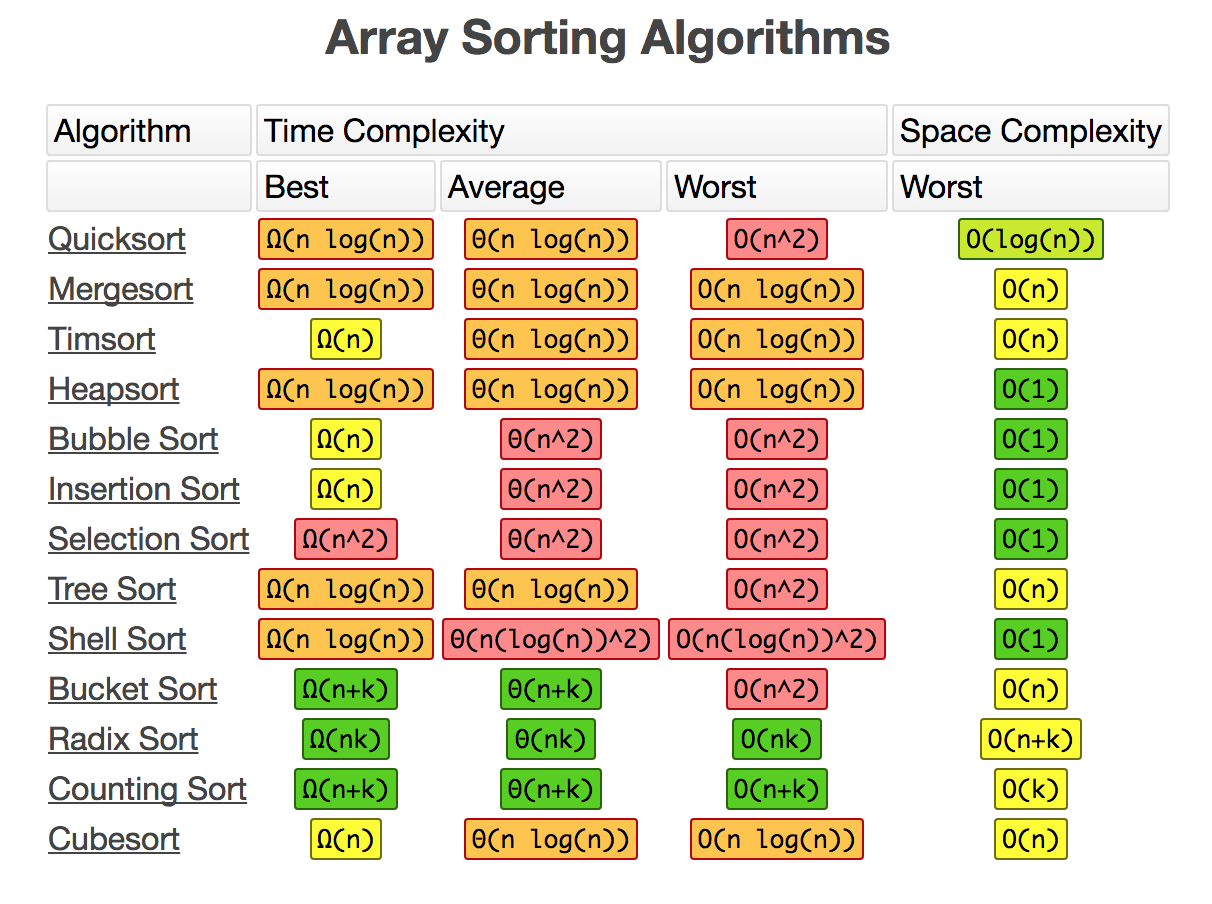
버블소트
const bubbleSort = array => {
let swapped;
do {
swapped = false;
array.forEach((number, index) => {
if (number > array[index + 1]) {
[array[index], array[index + 1]] = [array[index + 1], array[index]];
swapped = true;
}
});
} while (swapped);
return array;
};
function _bubbleSort(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
const less = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = array[j];
array[j] = less;
}
}
}
return array;
}삽입정렬
const insertionSort = array => {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (array[i] < array[j]) array.splice(j, 0, array.splice(i, 1)[0]);
}
}
return array;
};선택정렬
function selectionSort(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
let indexOfMin = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++)
if (array[j] < array[indexOfMin]) indexOfMin = j;
if (indexOfMin !== i) {
let less = array[indexOfMin];
array[indexOfMin] = array[i];
array[i] = less;
}
}
return array;
}퀵정렬
const quickSort = array => {
if (array.length < 2) return array;
const pivot = array[array.length - 1];
const left = [],
right = [];
for (let i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
if (array[i] < pivot) left.push(array[i]);
else right.push(array[i]);
}
return [...quickSort(left), pivot, ...quickSort(right)];
};병합정렬
const mergeSort = array => {
if (array.length < 2) return array;
const middle = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
const left = array.slice(0, middle),
right = array.slice(middle, array.length);
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
};
const merge = (left, right) => {
const result = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) result.push(left.shift());
else result.push(right.shift());
}
while (left.length) result.push(left.shift());
while (right.length) result.push(right.shift());
return result;
};
function _mergeSort(array) {
if (array.length === 1) return array;
const center = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
const left = array.slice(0, center);
const right = array.slice(center);
return _merge(_mergeSort(left), _mergeSort(right));
}
function _merge(left, right) {
const results = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] < right[0]) results.push(left.shift());
else results.push(right.shift());
}
return [...results, ...left, ...right];
}계수 정렬(카운팅 소트)
const countingSort = (array, max) => {
const counts = new Array(max + 1);
counts.fill(0);
array.forEach(value => counts[value]++);
const result = [];
let resultIndex = 0;
counts.forEach((count, index) => {
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
result[resultIndex] = index;
resultIndex++;
}
});
return result;
};검색 알고리즘
이진탐색
const binarySearch = (array, value) => {
const midIndex = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
const midValue = array[midIndex];
if (value === midValue) return true;
else if (array.length > 1 && value < midValue)
return binarySearch(array.splice(0, midIndex), value);
else if (array.length > 1 && value > midValue)
return binarySearch(array.splice(midIndex + 1, array.length), value);
else return false;
};
function _binarySearch(nums, target) {
// see if target appears in nums
// we think of floorIndex and ceilingIndex as "walls" around
// the possible positions of our target, so by -1 below we mean
// to start our wall "to the left" of the 0th index
// (we *don't* mean "the last index")
var floorIndex = -1;
var ceilingIndex = nums.length;
// if there isn't at least 1 index between floor and ceiling,
// we've run out of guesses and the number must not be present
while (floorIndex + 1 < ceilingIndex) {
// find the index ~halfway between the floor and ceiling
// we have to round down, to avoid getting a "half index"
var distance = ceilingIndex - floorIndex;
var halfDistance = Math.floor(distance / 2);
var guessIndex = floorIndex + halfDistance;
var guessValue = nums[guessIndex];
if (guessValue === target) {
return true;
}
if (guessValue > target) {
// target is to the left, so move ceiling to the left
ceilingIndex = guessIndex;
} else {
// target is to the right, so move floor to the right
floorIndex = guessIndex;
}
}
return false;
}이진탐색 트리
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
insert(data) {
if (data < this.data && this.left) this.left.insert(data);
else if (data < this.data) this.left = new Node(data);
else if (data > this.data && this.right) this.right.insert(data);
else if (data > this.data) this.right = new Node(data);
}
search(data) {
if (this.data === data) return this;
if (this.data < data && this.right) return this.right.search(data);
else if (this.data > data && this.left) return this.left.search(data);
return null;
}
}
728x90